Application of HEMO’s stent retriever FlexTake/CerebrAX in anterior and Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) thrombectomy
Surgeon Introduction

Liu Jian
Xuzhou first people’s hospital
- Associate Director of Interventional and Vascular Surgery, Chief Physician, Master of Medicine
- Member of Interventional Physicians Branch of Jiangsu Medical Association
- Member of the Neurointerventional Group of Jiangsu Interventional Society
- Member of the Hemorrhagic Cerebrovascular Disease Professional Committee of Jiangsu Stroke Society
- Young Member of Interventional Medicine Professional Committee of China Research Hospital Association

Li Hongyu
Xuzhou First People’s Hospital
Member of Xuzhou Stroke Association Neurointerventional Committee and Xuzhou Nuclear medicine Association Cancer Minimally Invasive Committee. Won the second prize of Xuzhou New Technique Introduction.
Specialty: Expert at interventional diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases, including: diagnosis and interventional treatment of acute stroke, cerebrovascular stenosis, intracranial aneurysm and cerebrovascular malformation; Rich experience in interventional therapy of peripheral vascular and tumor, such as interventional therapy of hepatic malignant tumor and malignant obstruction of biliary tract, interventional therapy of venous thrombosis and interventional therapy of peripheral arterial vessels.
Publication: Published 5 academic papers in Chinese mainstream journals, a number of entries in the Chinese series of magazines.
Case information
Patient chief complaint: Male, 69 years old, sudden left eye vision impairment for 2 hours
History of present illness: He had a sudden episode of blurred vision in his left eye 2h ago without any obvious inducement.
Past medical history: Grade 3 hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and postoperative status of cervical spine instrumentation.
Examination: Clear mind, normal speech, bilateral pupils of 4mm in diameter, normal light reflex, symmetrical nasolabial fold, tongue extension centered, muscle strength grade 5, normal muscular tension, tendon reflexes (+), and pathology (-).
Diagnosis:
1. Central retinal artery embolization
2. High Blood Pressure Level 3
3. Type-2 diabetes mellitus
4. Postoperative status of cervical spine internal fixation
Preoperative preparation
Severely twisted left carotid artery
The origin of the ocular artery was severely distorted, and the microcatheter could not be successfully superselected into the ocular artery after several times of shaping the guide wire and catheter
Surgical objective
The left Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) of the patient was moderately narrow at the beginning of the left ICA, and the distal vessel was not visible. It was considered that the thrombus was separated into the ophthalmic artery and caused the central retinal artery to be embolized. The left carotid artery was twisted seriously. Therefore, the 6F intermediate catheter was used for the ophthalmic artery catheterization.
Surgical procedures
Due to the serious distortion at the beginning of ophthalmic artery, the microcatheter could not be successfully superselected into the ophthalmic artery after multiple reshaping of the guidewire and catheter, and the patient had slow response, aphasia, and right limb weakness during the operation. Transcatheter ICA angiography revealed a marked filling defect in the left M1-M2 and A1-A2 segments of the MCA and slow distal flow, which was considered to be an acute occlusion of the MCA and the anterior cerebral artery due to re-detachment of a large vascular thrombus.
After replacement, TracLine / EmerAX 088-100 was delivered to the distal petrous segment of the left ICA and TracLine / EmerAX 071-130 to the spongy sinus segment of the ICA. TracLine 071-130 was delivered to the distal M2 segment of the MCA through the thrombus segment. Distal blood flow is unobstructed, suggesting that the MCA thrombosis is located near the M1-M2 section.The stent retriever FlexTake / CerebrAX 4*20mm intracranial embolectomy stent is delivered into the thrombus segment for release. After 5 minutes, the stent was withdrawn and aspiration was carried out at the same time. Massive thrombus was found on the stent, and angiography showed that the blood flow of the MCA M1-M2 and distal vessels was restored.
The left anterior cerebral artery was found to be nonvisible by contrast imaging, and the anterior cerebral artery thrombectomy was performed again. Due to the large tortuous angle in sections A1-A2 of the anterior cerebral artery, the Afentta / AsprAX 045-134 aspiration catheter was replaced and sent to the distal end of section A1 of the anterior cerebral artery. The microcatheter was sent to section A2 under the guidance of the microguide wire, and the FlexTake / CerebrAX 4*20mm intracranial thrombectomy stent was sent to section A2 for half release. After 5 minutes of stabilization, concurrently, negative pressure Afentta / AsprAX aspiration is used to withdraw the stent from the body. There were many thrombus on the stent, and thin strip thrombus was aspirated, and then angiography showed that the A1 segment of the anterior cerebral artery was unobstructed, and a small number of filling defects were seen in the A2 segment, with blood flow to the distal end. Tirofiban 9m/h was continuously administered into the antiplatelet therapy. 10 minutes later, the angiography showed that the blood flow in the MCA and the distal end was smooth, the filling defect in the A2 segment of the anterior cerebral artery was reduced, and the distal blood flow was increased. Then the antiplatelet drug was continued to be pumped and the patient waited for another 10 minutes. Post-angiography showed that the left MCA and distal blood flow were smooth, the filling defect of the A2 segment of the anterior cerebral artery was reduced, the distal blood flow was significantly increased, no obvious branch blood embolism was observed, and the blood flow reached grade 3.
Surgical procedure
Thrombus shadows were seen in the anterior and middle cerebral arteries, and the distal blood flow was slow
Swiftly replace TracLine / EmerAX 088-100 and 071-130, and pass the microcatheter and microguide wire through the thrombus segment to tighten the cavity
The FlexTake / CerebrAX intracranial thrombectomy stent 4*20mm was sent to the distal end of the brain for release in the M1-M2 segment
After thrombectomy support remained for 5 minutes, support was withdrawn, and negative pressure aspiration was performed to remove support from the body

A large number of thrombus were found on the stent. Angiography showed that the blood flow of the MCA M1-M2 and the distal vessels recovered, while thrombus was still found in the A2 segment of the left anterior cerebral artery
The left anterior cerebral artery did not develop, so the anterior cerebral artery was removed again. Due to the large tortuous angle of the anterior cerebral artery A1-A2, Afentta / AsprAX 045-134 was replaced and sent to the distal end of the anterior cerebral artery A1, and the microcatheter was sent to the A2 segment under the guidance of the microguide wire
FlexTake / CerebrAX intracranial thrombectomy scaffold 4*20mm was sent to segment A2 for half-release, and the thrombectomy scaffold was withdrawn while Afentta / AsprAX 045-134 was vacuumed with negative pressure to withdraw the scaffold
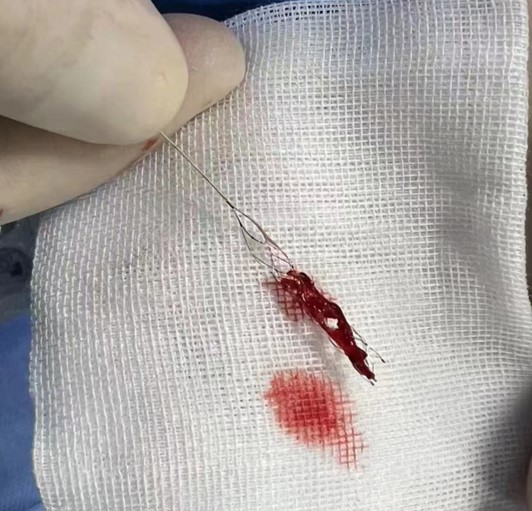
Large contrast imaging showed that the left anterior cerebral artery had restored blood flow
Anterolateral and lateral imaging showed that blood flow in the anterior and middle cerebral arteries was restored, and there was no sign of distal embolism
Postoperative imaging
Immediate postoperative CT showed no signs of intracranial infarction or hemorrhage
CT 6h after operation showed no signs of intracranial infarction and bleeding
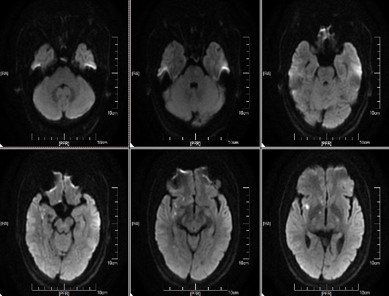
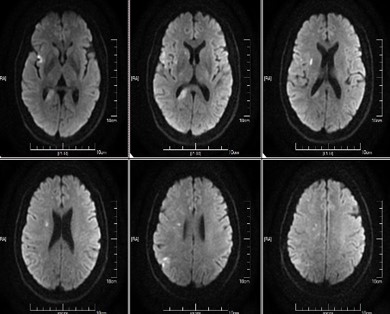
Review
The right upper and lower limb muscle strength was grade 4.
After rehabilitation training, patient recovered muscle strength after 1 month.
Case Summary
Case characteristics:
1.The patient had severe carotid artery tortuosity.
2.The anterior cerebral artery and the MCA were embolized respectively, both of which required rapid embolectomy to restore blood flow.
3.Because the function area of the MCA is many and important, the first choice is to restore the blood flow there.
Surgical Technique Essentials:
1. Due to the tortuosity of carotid artery, it is necessary to select a flexible catheter to establish the access.
2. The angle of the anterior cerebral artery was large, and the stent with good pushing and anterograde was selected, and the stent semi-release technique was used to reduce the traction injury potentially caused by the stent.
Equipment Use Skills:
1. Coaxial technique of TracLine / EmerAX 088-100 and TracLine / EmerAX 071-130 intravascular access catheter, Afentta / AsprAX 045-134 intracranial thrombus aspiration catheter to establish access, can reach a higher position and less vascular stimulation, for surgery to provide a good access;
2. FlexTake / CerebrAX intracranial embolectomy stent. The passability, visualization and thrombus grasping ability were good, which provided a reliable guarantee for the rapid reopening of cerebral blood flow in the middle and anterior cerebrum.
About Hemo Bioengineering
Hemo Bioengineering Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “Hemo”) officially commenced operations in 2017. Hemo’s global headquarters are located in Singapore, with R&D centers in US, Singapore and China. The company maintains long-term collaborations with US-based R&D laboratories to ensure the design of new products aligns with cutting-edge global technologies.
Hemo is dedicated to leveraging global high-quality R&D, production, clinical, and academic resources to provide innovative vascular and neurological interventional products. These products aim to serve doctors and patients worldwide by offering comprehensive interventional treatment solutions for cerebrovascular diseases such as ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, and intracranial vascular stenosis.

